Amazon Web Services (AWS) has announced a new strategic collaboration with Novartis that will transform the pharma giant’s core supply chain, manufacturing, and delivery operations through the use of AWS services.
AWS said the company will be helping Novartis transform its manufacturing process by unifying access to all information and enabling Novartis “to make quick and informed critical decisions”.
What follows is an excerpt of the blog AWS published to explain the manufacturing transformation it plans for Novartis.
Manufacturing transformation
In recent years, targeted and more effective therapies and vaccines have been made possible by new biologic molecules.
These "large molecule" therapies can be more complex to manufacture and can create new logistical challenges since they include living organisms.
Pharmaceutical companies strive to reduce the cost of manufacturing their “small molecule” therapies as those drugs lose patent protection while needing to scale up production to address the growing demand from developing markets, such as China.
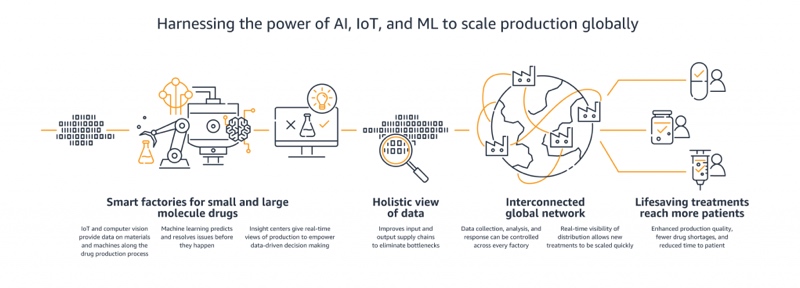
Infographic as seen on AWS website
Moreover, the manufacturing process has historically been focused on producing very large quantities of a particular therapy. Newer, genetically engineered therapies are designed for smaller cohorts, and may even be personalised down to an individual level.
Real-time data
The combination of these challenges requires manufacturers to make their upstream supply chains, manufacturing processes, and downstream distribution more visible, predictable, efficient, and adaptable.
For many AWS customers, the ultimate goal is an automated system that responds in real-time to all relevant information. This is true not just at the factory level, but also at the enterprise level: managers want to see throughput data for all factories globally to ramp certain production lines up or down, thereby minimising drug shortages and optimising capacity.
Amazon said it has spent years developing a sophisticated supply chain and automation systems that enable millions of products to be delivered to hundreds of millions of individuals, within hours.
Engineers know production lines inside and out, but have lacked the operational metrics to support moving from anecdotal to data-driven decision-making
In March of this year, for example, AWS and Volkswagen announced a collaboration to transform automotive manufacturing. When Novartis inquired about a potential collaboration in manufacturing and supply chain, the AWS Life Science practice saw an opportunity to help a pharmaceutical industry leader positively impact the lives of millions of patients.
Novartis is a large multinational medicines company, operating more than 60 manufacturing sites that produce therapeutics used by nearly 1 billion patients in 155 countries, annually.
Like any modern manufacturer, site control systems provide operational metrics to site managers about the efficiency of individual machines and facilitate day-to-day maintenance tasks.
Shift handover is a mission-critical point where information about operational performance is transferred from one crew to another. Engineers know production lines inside and out, but have lacked the operational metrics to support moving from anecdotal to data-driven decision-making.
Across the Novartis Technical Operations (NTO) group, it has been difficult and costly to develop standard metrics for global site efficiency, see the global operational performance in a “single pane of glass “, and build advanced machine learning models to predict site performance.
Operational strength
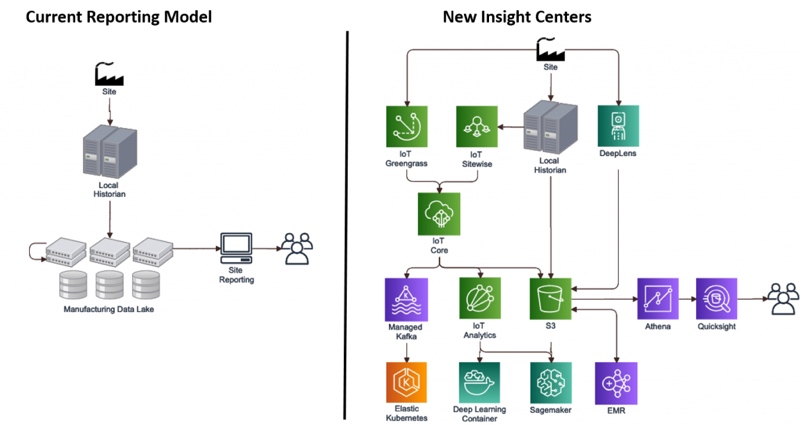
Prior to this collaboration, Novartis manufacturing site metrics had already been centralised into a traditional Hadoop-based big data platform, which has enabled the creation of extensive operational reporting.
Data is periodically ingested from local historians into Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS), where it is batch processed and prepared for reporting. While this has delivered value to the business, the operational reports are based upon fixed datasets which may be out of date in relation to operational decision-making.
Due to the use of legacy third-party vendors, this batch mechanism has not scaled to meet the needs of the business, including more users, additional metrics, advanced analytics and Machine Learning, and real-time data stream processing.
AWS and Novartis are jointly developing “Insight Centers” that provide real-time, interactive operational information to both site operators and corporate users
Through this collaboration, AWS and Novartis are jointly developing “Insight Centers” that provide real-time, interactive operational information to both site operators and corporate users around the globe.
Insight Centers ingest site operational metrics through existing components, such as local and global historians – platforms that capture industrial sensor data and add context and environmental meaning – as well as through new sensor integration.
Existing historians will supply data from “brownfield” sensors through nearly 20 SAP systems while AWS IoT Greengrass edge devices will deliver richer data sources, such as images and video, and all data will be stored on Amazon S3.
Besides the highly available and low-cost object storage for this data, AWS IoT Core and IoT analytics provide data forwarding to an IoT optimised time-series database where Novartis can perform real-time interpolation to facilitate predictive models.
Insight Centers will provide a cloud-native and ultra-scalable environment where existing big data processing technology can be run with minor changes due to compatibility with the most common frameworks and tools, but at a lower cost, and enabling new uses cases that weren’t previously possible like computer vision powered line inspection.
Daily production line and site operations will move to real-time data feeds, and add risk assessment models for proactive maintenance. Each site Insight Center will integrate with the others, providing a global view of the production capacity for each therapy.
Finally, global Insight Center integration will deliver per product and process traceability, including manufacturing status, inventory levels, and cost.
Infographic as seen on AWS website
As the volume, variety, and veracity of real-time data flow into the Insight Centers increases, the AWS AI/ML services will enable Novartis to create sophisticated ML models to advance its operational forecasting.
For AWS, the proposed technical architecture will create dynamic and flexible views of the Novartis global manufacturing processes. Novartis will soon be able to fully leverage AWS’s machine learning and AI services to predict machine failure, develop digital twins, and build forecasting models of demand that will enable more efficient supply.
These sophisticated use cases build upon the current initiatives already underway at Novartis. For example, Novartis is currently using Amazon SageMaker to build a computer vision-based model that will determine line clearance.
Amazon SageMaker is a fully managed service that covers the entire machine learning workflow to label and prepare data, develop an algorithm, train the model, tune and optimise it for deployment, make predictions, and take action.
Transforming manufacturing will add value to Novartis operations, and will ultimately deliver the most important value to patients receiving Novartis therapies. This transformation roadmap will enable a future where small batch and even personalised treatments can be developed and manufactured faster, with higher quality, lower costs, and delivered on schedule.
