Hermes Pharma, the expert in user-friendly solid oral dosage forms, has announced the commercial implementation of hot melt coating (HMC) in its production facility. The implementation of this technology is the result of a research project aimed at developing new pharmaceutical formulations that are stable, effective and user-friendly.
Acetylcysteine (NAC), a thermosensitive mucolytic compound exhibiting an unpleasant sour and metallic taste, was selected as the model active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) for this research project. The dosage form designated was orally disintegrating granules (ODGs), which consist of small granules that are applied directly into the mouth. ODGs do not require any water and are easy to swallow - even for people with difficulties swallowing tablets. As they do not have to be swallowed whole and spend more time in the mouth than conventional tablets, they are more thoroughly tasted, making taste-masking crucially important.
Hermes Pharma successfully deployed HMC to mask the sour and metallic taste of NAC, as well as its sulfuric smell, which are specific to this API. It also achieved a stable, immediate release profile and unaltered polymorphic form of the coating during storage (see Figure 1).
HMC was originally developed in the food industry. Among other purposes, it has been used to coat seasoning mixes in convenience food to minimise their hygroscopicity and thus volatilisation of the flavour during the logistic chain and prior to consumption. Flavour is only released upon heating, but not beforehand, improving taste, smell and quality of ready-made meals. HMC is a solvent-free coating technology that offers very short processing times (depending on the API, coating thickness and scale), and lower costs. It is also more eco-friendly than conventional coating methods. HMC involves covering the API solid core with a molten coating material at a carefully controlled temperature. This then solidifies to create a homogenous coating (see Figure 2).
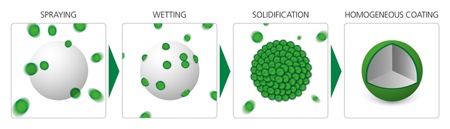
Figure 2: The illustration shows the HMC process, from spraying through to the finished coating. In the first step, the coating constituents are heated up and melted. Following this, the coating droplets are sprayed onto the seed particle (API) and wetting occurs on the surface. As the seed particle is colder than the melting temperature of the coating mixture, the droplets solidify and form a homogeneous layer
Thanks to this research project, a number of technical hurdles have been overcome. By applying Quality by Design (QbD) and using Process Analytical Technology (PAT) methods the progress and endpoint of coating can now be determined in real time. In particular, Hermes Pharma uses near-infrared spectroscopy (NIR) to monitor and control the coating process inline. This saves time and improves quality.
HMC is now a proven technology to mask the unpleasant taste and smell, which patients often experience when pharmaceuticals dissolve in the mouth. The technology has been upscaled from laboratory to production, meeting the strict standards for pharmaceutical production (GMP), and can be transferred to other APIs. The coated API can be easily blended with excipients and flavours, as well as other APIs for tailor-made products to suit customer requirements and deliver further medical benefits. HMC technology could also be applied to other dosage forms, for example Orally Disintegrating Tablets (ODTs) and Multiple Unit Pellet System (MUPS). Two related patents have been successfully filed.
'We believe that our scientific know-how has led us to prove our technological and production leadership, resulting in being the first company to make HMC commercially available for the pharmaceutical industry,' said Dr Detlev Haack, Director Research & Development at Hermes Pharma. 'Our industrial customers will benefit from products that are truly user-friendly and deliver real value to patients and consumers.'
Patient adherence to a medication regime impacts the therapeutic outcome. Based on recent data resulting from a study commissioned by Hermes Pharma, ODGs and other user-friendly dosage forms have been found to be a welcome alternative to conventional dosage forms. They offer patients with swallowing difficulties, including children and the elderly, a user-friendly alternative that can lead to better compliance thus reducing healthcare costs.
Initiated by Hermes Pharma in 2012 in conjunction with the Research Center Pharmaceutical Engineering GmbH (RCPE), INNOJET Herbert Hüttlin and the Karl Franzens University Graz, Department of Pharmaceutical Technology, the collaboration has now been completed as planned. Hermes Pharma recently won the Research and Innovation Award, the highest recognition that the Carinthian Economic Promotion Fund of Austria awards in this field for its research into Hot Melt Coating.

