Despite its maturity, the softgel market is looking stronger than ever and still offers massive potential for development.
A recent report valued the global softgel market at $1.1 billion in 2023 in terms of revenue … and predicted that it will grow by an average of 6.3% annually for the next few years to reach $1.5 billion by 2028.1
This is substantial growth for an established market and several factors are driving this continued expansion. Chief among these is a heightened interest in health and wellness, with more consumers prioritising their well-being and taking a proactive approach to self-care and health management.
Supplement industry soft on softgels
This has sent demand for nutritional supplements on an upwards trajectory; softgels are often the preferred format for these products as they offer a convenient, efficient and consumer-friendly way to deliver both liquid and semisolid ingredients.
They are suitable for the encapsulation of a wide range of compounds, from vitamins and minerals to omega-3 oils, botanical extracts and CBD.
Softgels have always enjoyed high acceptance rates among consumers and many people prefer them as opposed other dosage formats because they are easy to swallow and convenient to take.
High bioavailability
Plus, they have other attributes that are progressively coming into play as supplement usage gets more sophisticated. Proof of efficacy is evermore important; consumers are increasingly savvy and only want to spend their hard-earned cash on supplements that are proven to work.
Therefore, thanks to their excellent bioavailability, softgels are an ideal choice. From a manufacturer’s point of view, they are an attractive dosage form because softgels can be used for oil-based ingredients to provide fast and effective drug delivery.
The hermetic seal that is created during softgel manufacture also contributes to their superior performance. It helps to protect sensitive compounds from moisture and oxygen, preserving their potency throughout a longer shelf-life.
A perfect dose
All the qualities that make softgels attractive to consumers also ensure their popularity with manufacturers — not only in the dietary supplement space but also in the pharmaceutical industry.
Here, softgels offer a route to market for drugs with low aqueous solubility as well as enabling highly accurate dosing and optimal delivery of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs).
Moreover, advancements in capsule manufacturing technologies, such as improved formulations, enhanced stability and faster dissolution rates, are contributing to market expansion.
Gelatin: a firm favourite
Gelatin is the most widely used excipient in the softgel industry.2 There are several reasons why it’s popular with both manufacturers and consumers.
The former are increasingly cautious about what they put on their ingredient lists … and rightly so. At the start of this year, Innova Market Insights named natural ingredients as one of the key trends of 2024.3
The researcher noted that consumers may be open to foods and beverages that are made with natural ingredients and that highlight these in their labelling and on-pack promotion.
It also stated that honesty and transparency are important values, with one third of consumers checking for ingredients of interest on a product label. Gelatin aligns with this trend.
It is a clean label ingredient that is safe, trusted and non-allergenic. As a natural source of protein that’s easily digested, it’s also considered to be a healthy ingredient. The smooth, easy-to-swallow texture of soft gelatin shells adds to their consumer appeal.
Top technical attributes but certain stress factors
From a manufacturing perspective, gelatin is an easy and versatile material to work with. As well as being highly soluble, it offers excellent mechanical strength and seal quality owing to its low setting/melting point.
Because of this low melting temperature (approximately 37 °C), gelatin is gentler on the fill than plant-based alternatives (70–80 °C) and makes the production process safer and more resource efficient.
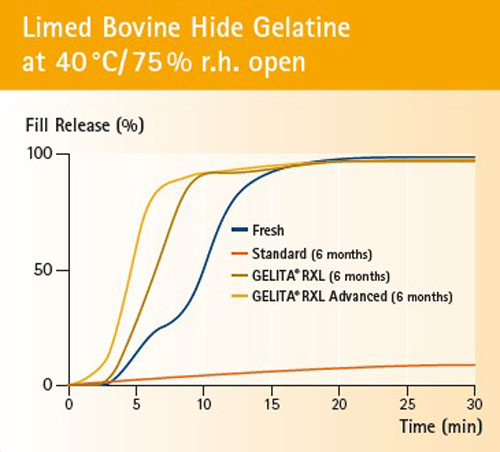
Figure 1: Six-month-old RXL and RXL Advanced capsules release their fill significantly faster than fresh and/or stored standard gelatin capsules.
It also has a high oxygen barrier, which is especially beneficial for oil-based active ingredients such as polyunsaturated fatty acids.
However, there are certain stress factors that can affect the performance of gelatin softgels, including extended shelf-life requirements, problematic fills and extreme storage conditions.
According to the ICH guidelines for stability studies, the world is divided into five climatic zones (I, II, III, IVa and IVb). Countries with temperate climates fall into zone I whereas, at the other end of the scale, countries with hot and humid climates (most of the Asia-Pacific region) are classed as zone IVb.
Exposure to these extreme climatic conditions can have a detrimental effect on softgel stability and shelf-life.
Dangerous liaisons: crosslinking
One of the issues that can occur in hot and humid conditions is crosslinking of the gelatin shell. There are two types of crosslinking: self-crosslinking — when the gelatin reacts with itself — and (externally) induced intra-crosslinking — when the gelatin interacts with active ingredients.
Self-crosslinking usually occurs during prolonged storage periods. Typically, the lysine side residues of amino acids bond with the carboxylic acid in the gelatin, forming crosslinks within the gelatin shell.
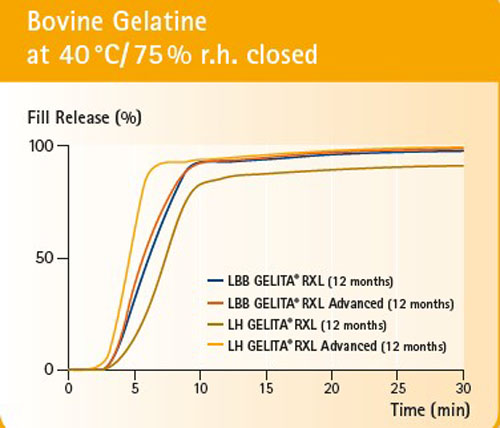
Figure 2: RXL Advanced reduces the crosslinking potential for critical fills to support controlled fill release performance throughout the product’s entire shelf-life.
Intra-crosslinking happens because the filling of the capsule reacts with the amine groups of amino acids that form the backbone of the protein. Some of the chemical structures that are likely to incite intra-crosslinking activity include aldehydes, ketones, polyphenols, phenols and peroxide intermediates.
These substances are often found in fruity/herbal extracts and in some vitamins (vitamin B2, for instance). Peppermint oil, an essential oil that’s known to be rich in ketones, is another example.
Undesirable consequences
Crosslinking can have various consequences that are detrimental to product quality, efficacy and performance. The shell can become hard, brittle and can even crack. It can also cause the formation of a water-insoluble membrane, known as a pellicle. This can impede the release of the fill, resulting in unreliable dissolution.
Self-protection strategy
The pharmaceutical industry is trying to find a way to reduce crosslinking with varying degrees of success. GELITA has taken a different approach and conceived a gelatin grade that essentially protects itself against crosslinking.
Branded RXL, this patented technology deactivates gelatin’s ability to interact with reactive molecules.
It does this by controlling the molecular weight distribution of the gelatin. Small, highly mobile gelatin molecules effectively block the crosslinking effects of the larger ones — much like interfering with the interaction between a key and its lock.
This so-called “scavenging” mechanism makes it unavailable for self- and intra-crosslinking reactions.
This technological breakthrough enables manufacturers to develop softgels with a longer shelf-life, improved stability under extreme conditions and enhanced dissolution properties … even when using demanding fills.
It means that brand owners can be confident that fill release will be consistent throughout the product’s shelf life. It also allows easier, more reliable product development and faster time-to-market by avoiding potential gelatin-fill interactions.
Pushing boundaries
GELITA has taken this technology one step further and developed a gelatin grade that ensures long-term capsule stability for critical fills. RXL Advanced minimises the crosslinking potential, which, in turn, provides reduced pellicle formation and supports controlled fill release performance throughout the entire shelf-life.
The performance of RXL has been proven in tests (Figures 1 and 2). After 6–12 months of storage at stress conditions (40 °C/75% rh), the soft capsules made from RXL and RXL Advanced gelatins demonstrated the same fill release compared with fresh standard gelatin capsules produced and stored under the same conditions.
Zero crosslinking
GELITA’s latest innovation is RXL Ultra, an optimised gelatin that eliminates crosslinking completely. It does this by masking the free amino groups of lysine and hydroxylysine through a covalent bonding with succinic acid.
This means that these free amino acids are no longer available to participate in crosslinking reactions. This breakthrough has created a new “gold standard” in crosslinking prevention. It is currently only available for prescription products in the European Union.
A new frontier in softgel development
Demand for gelatin softgels is at an all-time high, buoyed by a rise in consumer awareness about the importance of preventive healthcare and coupled with the need for health management solutions that support an ageing population.
However, this potential can only be realised if the technical limitations of gelatin as a softgel excipient can be overcome.
The strides that GELITA has made with its RXL portfolio have gone a long way to addressing the issue of crosslinking … but there are still issues to be solved. The coming years are sure to see some exciting development in this field, particularly in dietary supplements.
References
1. www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/softgel-capsules-market-238329912.html.
2. www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/softgel-capsules-market.
3. www.innovamarketinsights.com/trends/ingredients-trends/.
